Important Definitions
- Law of conservation of mass: Mass can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction. That means total mass of reactants is equal to total mass of product. If 12g carbon react with 32g of oxygen , 44g of carbon dioxide will form.
- Law of definite proportion: The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass. This law is also known as Proust’s law or the law of constant composition. Example the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen in water is always 1:8, irrespective of the source and method of obtaining water.
- Ions: Element which carry charge is called ions. Element which carry positive charge is called cations and the elements which carry negative charge are called anions. Group of atoms containing charge is called polyatomic ions.
- Valency: The combining capacity of element is called valency. Valency is equal to number of electrons an element accepts or donates during chemical reaction.
- Atomic Mass Unit (a.m.u) or Unified Mass (u):One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one-welfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
- Atomicity: Number of atoms constituting a molecule or compound. Example oxygen is diatomic, phosphorus is tetra atomic.
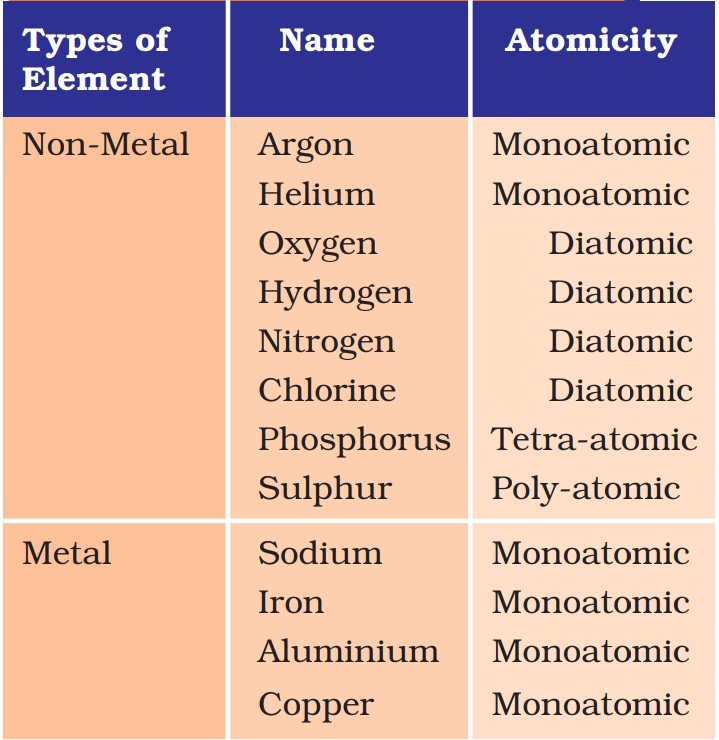
List of atomic masses:
| Elements | Atomic Mass (u) |
| C | 12 |
| N | 14 |
| O | 16 |
| Na | 23 |
| Mg | 24 |
| Al | 27 |
| P | 31 |
| S | 32 |
| Cl | 35.5 |
| Ar | 40 |
| K | 39 |
| Ca | 40 |
Dalton’s atomic theory:
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
List of important Elements
| Atomic Number | Element | Symbol |
| 1 | Hydrogen | H |
| 2 | Helium | He |
| 3 | Lithium | Li |
| 4 | Beryllium | Be |
| 5 | Boron | B |
| 6 | Carbon | C |
| 7 | Nitrogen | N |
| 8 | Oxygen | O |
| 9 | Fluorine | F |
| 10 | Neon | Ne |
| 11 | Sodium (Latin-Natrium) | Na |
| 12 | Magnesium | Mg |
| 13 | Aluminium | Al |
| 14 | Silicon | Si |
| 15 | Phosphorus | P |
| 16 | Sulphur | S |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl |
| 18 | Argon | Ar |
| 19 | Potassium (Latin-kalium) | K |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca |
Q. Define molecular mass.
Ans. The sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule or compound is called molecular mass. It SI unit is u (Unified mass). Molecular mass of NaCl= atomic mass of Na+atomic mass of Cl=23+35.5=58.5u. Molecular mass of CO2=atomic mass of C+2×(atomic mass of oxygen)=12+16×2=12+32=44u.
List of valencies of ions and polyatomic ions
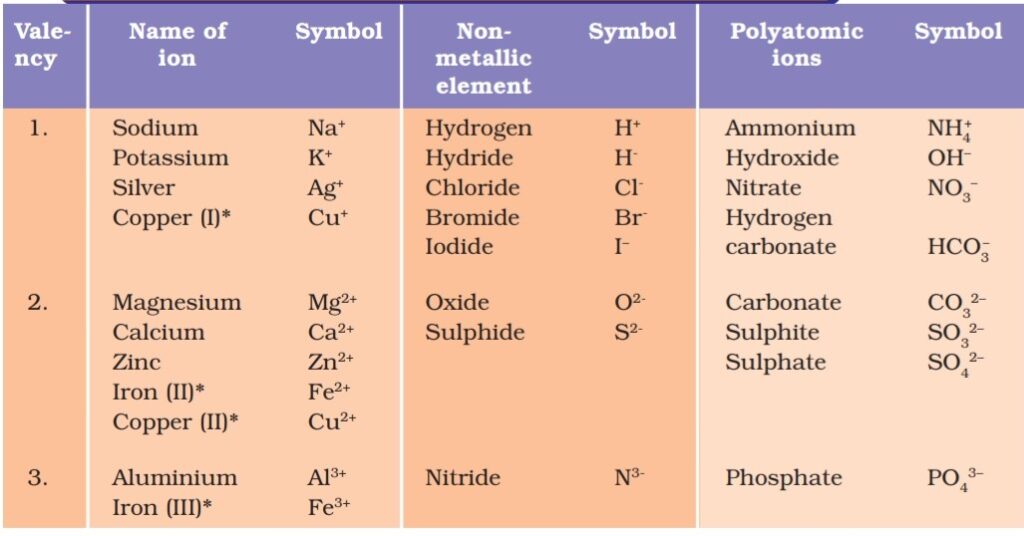
Q. How compounds are formed by using valency?
Ans. Writing formula is a technic. While writing formula of a compound you have write symbol of elements or ions. Assign valencies to each species. Cut the Valencies with common factor if have. Finaly cross multiply the valencies. If there is polyatomic ions bracket should be used if you multiply by 2 or more number.
Examples:

Q. What do means by formulas unit mass?
Ans. Formula unit mass is like molecular mass which is find for ionic compounds. For example formula unit mass of NaCl=23+35.5=58.5u.
Q. Find molecular mass of a. Quick lime b. Baking soda c. Lime stone.
Ans. a. Quick lime is Calcium Oxide, CaO. Molecular mass=40+16=56u. b. Baking Soda is Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate, NaHCO3. Molecular mass=23+1+12+16×3=74u. c. Lime stone is Calcium carbonate, CaCO3. Molecular mass=40+12+16×3=100u.
Q. Write atomicity of 1. H2O 2. NaNO3 3. Ca(OH)2
Ans. 1. 3 2. 5 3. 5
Q. 3g carbon react with 8g of oxygen to for 11g of carbon dioxide. What mass of carbon dioxide will form if 12g of carbon burn in 8g of oxygen?
Ans. 11g. As 8g of oxygen is present which react with only 3g of carbon due law of constant proportion. 12-3=9g of carbon left unreacted.