Q. Why a chemical reaction should be balanced?
Ans. A chemical reaction should be balanced to follow law of conservation of mass. That means total mass of reactants should be equal to total mass of product.
Q. What can be the possible changes during a chemical change during a chemical reaction?
Ans. The following changes can be occurred during a chemical reaction:
- Change in state , example gas changes into liquid
- Change in colour
- Change in temperature
- Evolution of gas
Q. Why magnesium ribbon cleaned before burning. Write reaction of combustion of magnesium.
Ans. Magnesium ribbon is cleaned before burning to remove a white layer of magnesium oxide that forms on its surface. This layer prevents the ribbon from burning.
Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame and changes into a white powder. This powder is magnesium oxide. It is formed due to the reaction between magnesium and oxygen present in the air.
2Mg+O2————>2MgO
Q.List the types of chemical reactions.
Ans. On the basis of heat exchange:
- Endothermic reactions
- Exothermic reactions
On the basis of arrangements of atoms:
- Combination reactions
- Decomposition reactions: a. Thermal decomposition b. Photo decomposition c. Electrolytic decomposition
- Displacement reaction
- Double displacement or precipitation reaction
On the basis of oxygen, hydrogen and electrons:
- Oxidation
- Reduction
Q. Compare endothermic and exothermic reactions.
Ans.
| Endothermic | Exothermic |
| A chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed by reactants or heat is provided to reactants to carry out a chemical reaction is called Endoplasmic reactions | A chemical reaction in which heat is released by reactants or heat is taken out from reactants to carry out a chemical reaction is called exothermic reactions |
| Example: decomposition reactions | Example: Respiration , combustion of fuel,decomposition of vegetable matter into compost. |
Q. Compare combination and decomposition reactions.
Ans.
| Combination Reaction | Decomposition Reaction |
| A chemical reaction in which two or more elements or compounds react to form a single bigger compound is called combination reaction. | A chemical reaction in which a single bigger compound is brocken down into simpler compounds or elements by heat , light or electricity is called decomposition reaction. |
| Examples: 1. C+O2———–>CO2 2. CaO+H2O————->Ca(OH)2 | Examples: Thermal Decomposition A. 2FeSO4‐————heat———->Fe2O3+SO2+SO3, ferrous sulphate changes color from light green to white on heating. B. CaCO3—————-heat———->CaO+CO2 C. 2Pb(NO3)2———–heat———->2PbO+4NO2+O2. , nitrogen dioxide NO2 is brown fume. Photo decomposition A. 2AgCl———sunlight—–>2Ag+Cl2 B. 2AgBr——–sunlight——->2Ag+ Br2. These reactions are used in black and white photography. Electrolytic decomposition 2H2O———electricity/H+(acid)——>2H2+O2. On acidic electrolysis of water , Hydrogen is obtained at cathode and oxygen is obtained at anode. Hydrogen obtained is of double volume as oxygen because two moles of H2 and one mole of oxygen is obtained. |
Q. Define (i) Displacement reaction (ii) Double Displacement reaction
Ans. (i)Displacement Reaction: A Reaction in which a highly reactive element displaces a less reactive element from it’s compound. For example a highly reactive metal displaces a less reactive compound from it’s salt.
K+CaSO4———>K2SO4+Ca
Fe+CuSO4———>FeSO4+Cu
Cu+ZnCO3———>No reaction, as Copper is less reactive than Zinc.
(ii) Double Displacement Reaction:A reaction in which exchange of ions takes place. In this reaction an insoluble precipitate (ppt) is formed, so called precipitation reaction.
Examples:
- Pb(NO3)2(aq)+KI(aq)————>PbI2(S)+KNO3(aq), lead iodide is precipitate (ppt)
- Na2SO4(aq)+BaCl2(aq)———–>NaCl(aq)+BaSO4(s) , Barium sulphate is precipitate (ppt)
- CuSO4 (s) + H2S (g) → CuS (s) + H2SO4 (aq).
Q. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Ans. (i) Substance X is quick lime or calcium oxide. Formula is CaO
(ii) CaO(s)+H2O———>Ca(OH)2, Ca(OH)2 is Calcium hydroxide or slake lime.
Q. Explain oxidation , reduction and redox reactions.
Ans. Oxidation: A reaction in which any one of the following is taking place is called Oxidation.
- Gain of oxygen
- Loss of hydrogen
- Loss of electrons
Reduction : A reaction in which any one of the following is taking place is called reduction.
- Gain of hydrogen
- Loss of oxygen
- Gain of electrons
Redox Reaction: A reaction in which both oxidation and reduction take place is called redox reaction.
Some important examples:
- Oxidation of copper to copper oxide: 2Cu+O2———heat—–>2CuO
- Reduction of CuO into Cu: when hydrogen gas is passed over this heated material (CuO), the black coating on the surface turns brown as the reverse reaction takes place and copper is obtained. CuO+H2——–heat—————–>Cu+ H2O
- Redox Reactions:
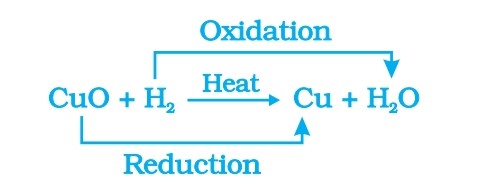
- Some other examples of redox reactions

Q.Define oxidizing and reducing agent
Ans. Oxidizing agent:The reactant which is getting reduced itself but oxidize other reactant.
Reducing agent: The reactant which is getting oxidized itself but reduces other reactant.
In following reaction:
ZnO+C———>Zn+CO, Here Zno is reduced to Zn so Zno is Oxidizing agent. It oxidises C to CO. And C is reducing agent as C is itself oxidize to CO and reduces ZnO.