Important definations
- Current: The rate of flow of charge is called current. It SI unit is called Ampere (symbol A). I=q/t. 1A of current is defined as 1 Coulomb of charge flowing through circuit per second.
- Charge on one electron is 1e= -1.6×10^-19 Coulomb.
- Charge on n of electrons, Q=ne.
- 1mole contain 6.022×10^23 particles called Avogadro Number.
- Potential: It is defined as work done to carry a charge from infinity to a point in electric field (circuit). It’s SI unit is volt. V=W.D/Q. 1volt is defined as to carry 1 Coulomb of charge from infinity to electric feild 1 Joule of work is done. 1 volt=1 Joule/1 Coulomb.
- Potential Difference: It is defined as work done to carry a charge from one point to another point in electric circuit. Numerically it is the difference between potential of any two point in electric circuit. It’s SI unit is also Volt. If potential difference, v=0, no current flowing through circuit. It is also called voltage.
Ohm’s law and it’s derivation
At constant temperature current flowing through circuit is directly promotional to potential difference.
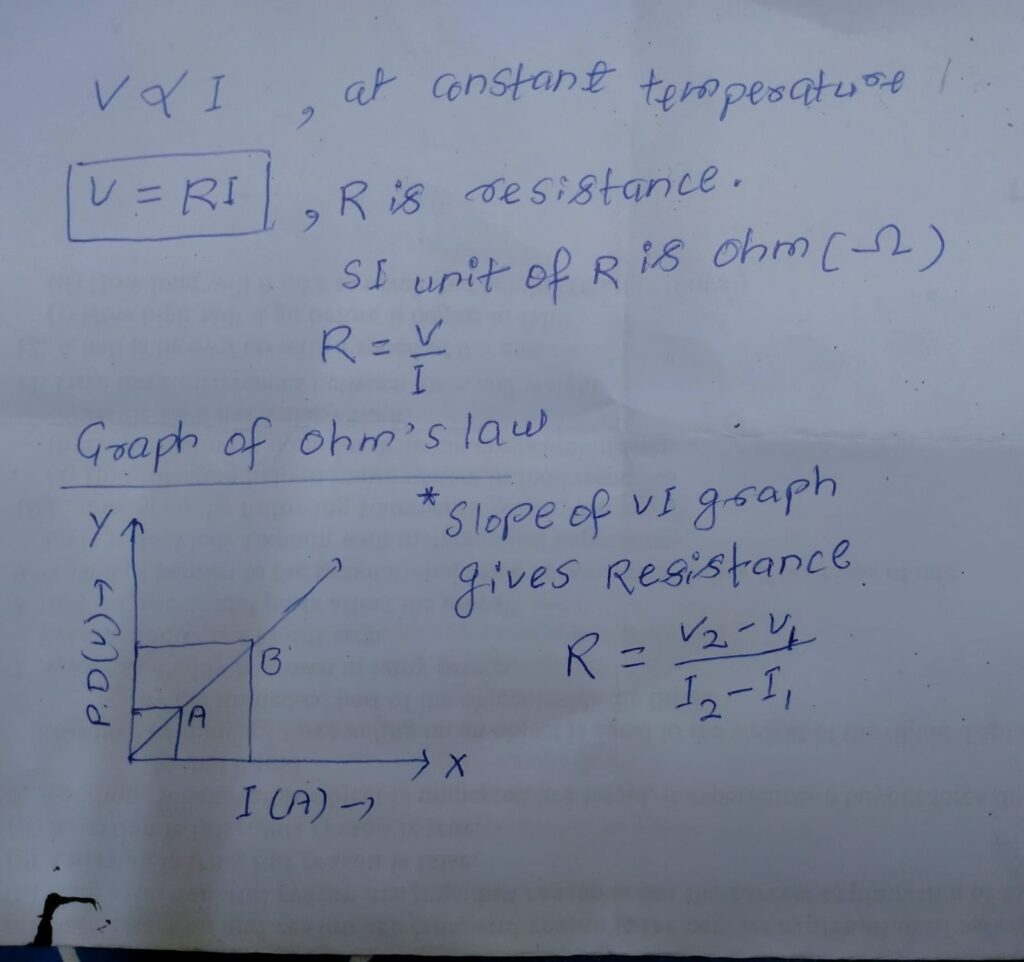
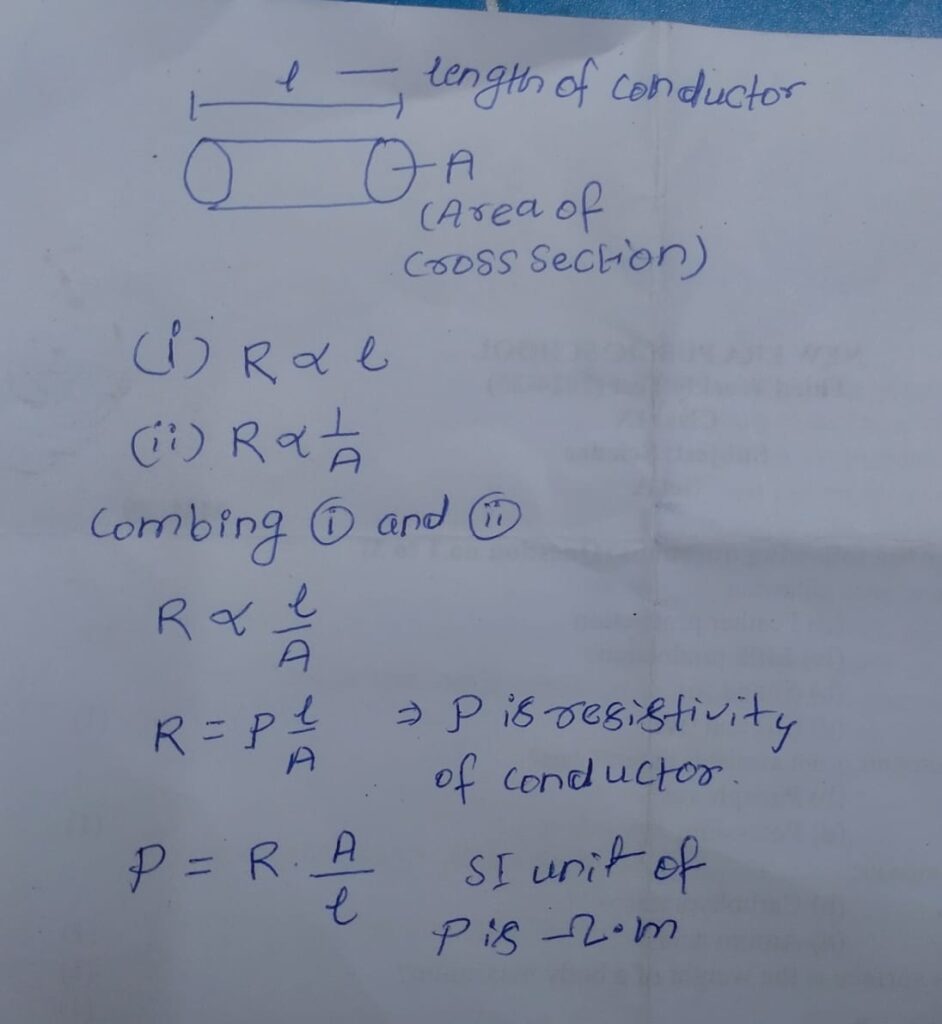
Q. Derive expression for resistivity.
- Resistance is directly propotional to the length of conductor.
- Resistance is inversely proportional to the length of conductor.
Important circuit diagrams:
COMBINATION OF 3 RESISTORS IN SERIES:
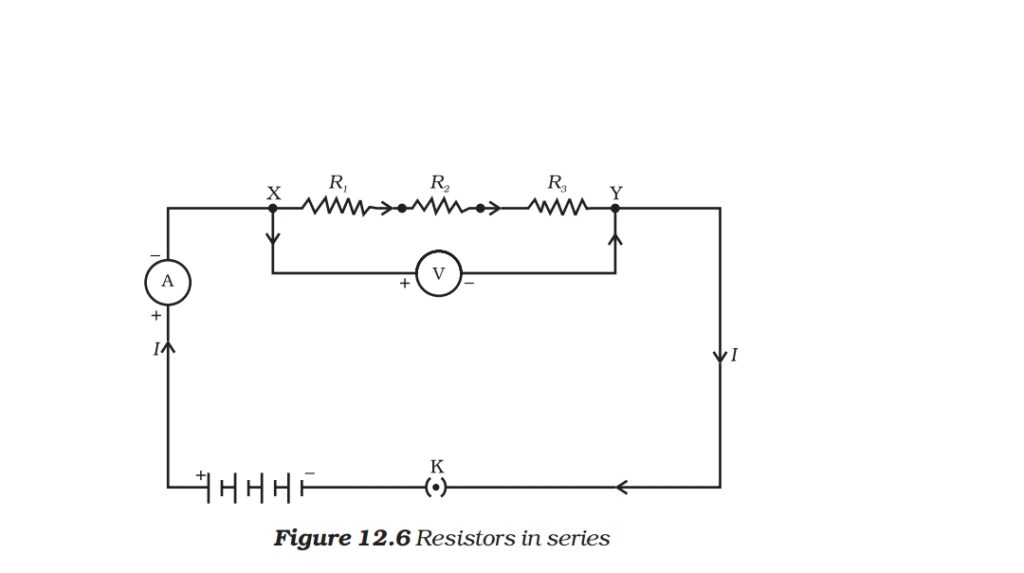
Q. Derive Req=R1+R2+R3.
Ans. In series combination:
1. Current remain for all resistors
2. Voltage distributed among resistor that means total voltage =sum of individual voltage, v=v1+v2+v3.

Combination of 3 resistors in parallel:
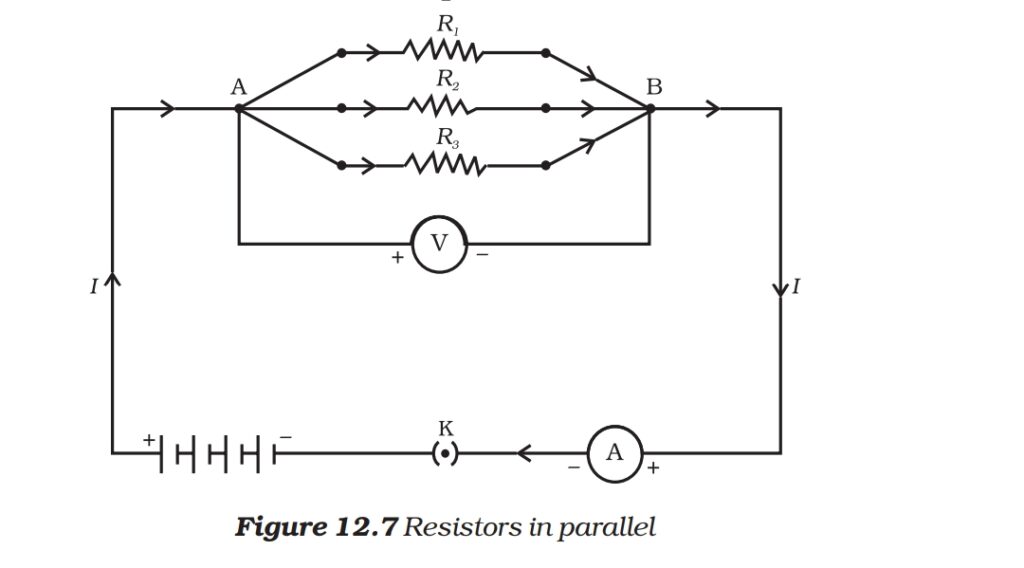
Q. Derive 1/Req=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3.
Ans. In parallel combination:
- Votage will be same for all resistors
- Current is divided among resistors that means I=I1+I2+I3.

Q. Write factors on which resistance of conductor depends.
Ans.
- Resistance is directly proportional to length of conductor.
- Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross section.
- Resistance directly depends on temperature
- Resistance depends on nature of material.
Q. On what factors resistivity depends?
Ans. Resistivity mainly depends on two factors:
- Nature of materials. Insulators have very high resistivity and conductors have low resistivity.
- Temperature: on increasing temperature resistivity of conductors increases.
Q. Explain Joule’s law of Heating?
Ans. Work done by electrons changes into heat energy.
There are three postulates of Joule:
- Heat is directly proportional to the square of current, when R and t are constant.
- Heat is directly proportional to resistance of conductor when I and t are constant
- Heat is directly proportional to time when R and I are constant

Q. Derive H= I^2Rt.
Ans.

Important formula list

Give reason:

Ans.
a.) Tungsten have melting point, which withstand at high temperature and do not melt. At very high temperature it starts growing with breaking. So it is used in bulb filament.
b.)Alloys have higher resistivity than pure Metals. Heat is directly proportional to resistance anc resistivity so heating devices like heaters, toasters and electric irons is made up of Alloys. For example nichrome an alloy of chromium and nickel is used in heater.
c.) Series arrangements is not proffered in domestic circuit due to following reasons:
- Breaking of wire at any point will stop working of remaining devices.
- different devices have different energy requirement which is not possible in series.
- Equivalent resistance in series combination is higher, that there will be loss of electricity in the form of heat.
d. ) Resistance of wire is inversely proportional to area of cross section. That means thicker wire have lower resistance.
e.) Due to following reasons copper and Aluminium are used as wire for electrical transmission:
- These Metals are good conductor of electricity.
- These Metals are ductile that they can be drawn into wires.
- These Metals are cheap and easily available.