Important Definitions
- Mixture: Substances which constituted by more than one kind of pure substance.
- Solution: homogenous mixture of two or more substances. Example sugar solution, salt solution. The solution has two components – solute (present in less quantity) and solvent. Solution =solute+solvent
- Alloy: Homogenous mixtures of metals. Brass is alloy of Zinc (30%) and copper (70%).
- Tyndall Effect: Scattering beam of light by the particles of colloid or suspension, and path of light visible. Example Tyndall effect can be seen (i) when when fine beam of light enters a room through a small hole.(ii)sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest.
- Element: Element is basic form of matter that can not be broken down into simplar substances by chemical reactions. Elements can be divided into Metals, Non Metals and metalloids. Silver, gold, iron, calcium etc. Most of elements are solid , 11 elements are gases at room temperature. Mercury and bromine are liquid at room temperature. Gallium and Caesium are liquid at 302K.
- Compounds: A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements, chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion. Examples water, ammonia, carbon dioxide, sodium chloride etc.
- Metalloids: Elements which have intermediate properties between metal and non metal are called metalloids. Examples Boron , silicon and germanium.
Write some important examples of solutions.
- Tincture of iodine: solid in liquid solution. Iodine (solid ) is solute and alcohol(liquid) is solvent.
- Sugar Solution: solid in liquid Solution. Sugar is solute and water is solvent.
- Soda water: gas in liquid Solution. Carbon dioxide is gaseous solute mixed with water (liquid).
Define air.
Ans. Air is homogeneous mixture of a number of gases. Main constituents of air are nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%) other important gases are argon, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
Properties of Solution:
- Homogeneous mixture of solute and solvent.
- Particle size is less than 1nano meter. Particles are so small that we can’t see through naked eye.
- It doesn’t show tyndall effect.
- Solution is stable that means particles do not settled down when left undisturbed.
- It can not be seperated through method of filtration as particles size is so less.
- Examples sugar solution, salt solution, tincture of iodine etc.
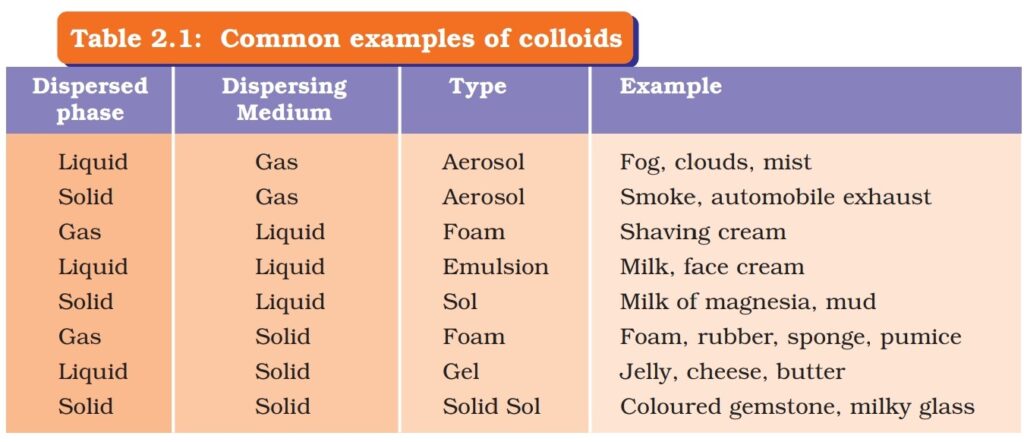
Properties of Colloid:
- It is heterogeneous mixture of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
- Particles size are 1nanometer to 1000nano meters
- Particle size is so small that we can’t see through naked eye.
- It shows tyndall effect that means particles of colloid can scatter beam of light.
- Colloids are stable that means particles do not settled down when left undisturbed.
- It can be seperated through ultra filter paper.
- Examples blood, milk, sol etc.
Properties of suspension:
- It is heterogeneous mixture
- Particles sizes are more than 1000nanometers.
- Particles size are big enough to see through naked eyes
- Particles of suspension can scatter beam of light that means suspension can show tyndall effect.
- Suspension are not stable that means particles settle down when left undisturbed.
- Particles can be seperated through naked eye
- Examples chalk in water, mud in water etc.
Compare compound and mixture:

Compare homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture:
| Homogeneous mixture | Heterogeneous mixture |
| Uniform composition throughout | Non uniform composition |
| examples sugar in water, salt in water , sulphur in carbon disulphide, water and alcohol. | Examples sand and salt, sugar and salt, wood, blood, oil in water. |
Q. Define concentration of solution.
Ans. Concentration of solution can be defined as percentage of solute present in the solution. It can be divided into mass/mass, mass/volume and volume/volume concentration.
m/m concentration =(mass of solute/mass of solution)×100.
m/v concentration =(mass of solute/volume of solution)×100
v/v concentration =(volume of solute/volume of solution)×100.
Example if 20g of solute is present in 120g solvent. Find m/m concentration.
mass of solution =20+120=140g
m/m concentration =(mass of solute/mass of solution)×100=(20/140)×100=100/7=14.2%.