Important Definitions
- A current carrying conductor behaves like a magnet , a magnetic compass is deflected when bring near a current carrying conductor.
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic field is area of influence of a Magnetic . It is a vector quality which have both magnitude and direction.
- Field Lines: The direction of magnetic field is shown through imaginary lines are called field lines.
- Electromagnet: The temporary magnet which are produced when shoft iron is placed inside a solenoid. Strength of electromagnet depends upon magnitude of current and number of turns of the coil.
- * One difference between permanent and electro-magnet is that the strength and polarity of electro magnets can be change whereas in permanent magnet strength and polarity are fixed.
- Right hand Thumb Rule(statement):place current carrying conductor in your right hand such a way that thumb shows the direction of current, the the direction of wrapping of fingers will show the direction of magnetic field. Right-hand thumb rule is also known as Maxwell’s corkscrew rule.

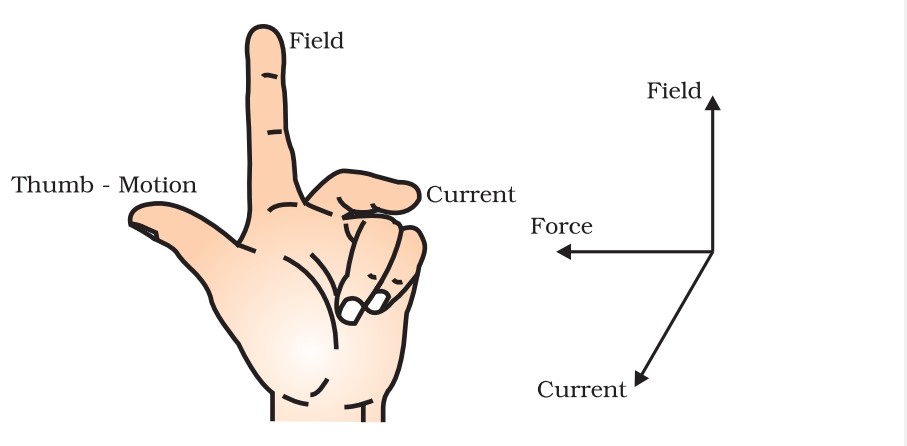
- 7. Fleming’s left hand Rule(statement): Strech fore finger, middle finger and thumb of your left hand such a way that they are mutually perpendicular. If middle finger shows the direction of current and fore finger shows the direction of magnetic field then thumb will show direction of force or motion.
- 8. Live wire: It is the main wire which carry the current from power source to domestic circuit. It is generally red in colour.
- 9. Neutral wire: It completes the circuit and carry unused current back to power station. It also maintain the voltage. It is generally black in colour.
- 10. Earth Wire: It works as safety device. It is generally green in colour. Earth wire send any leakage of current to earth and prevent any chance of electrical shock.
- 11. Overloading: When two many devices are connected at single source, too much of current is derived from the wire. This may lead to over heating of circuit.
- 12. Short circuit: When live wire and neutral wire comes in contact due to breaking of insulation lead to sudden increase of current, which causes sparks and may cause fire.
- Fuse: It is used as safety device. It works on the principle of heating effect of current. It is made up of material which have less melting point. It protects electrical circuits from damage caused by short circuits, overloading, or equipment failures.
- There are two types of current available in domestic circuit, one is 5A and another 15A. 15A socket is called power socket which used to operate AC, Refrigerator, geyser etc.
Magnetic field lines along bar magnet
- Field lines emerge from north and merge at south pole of magnet outside the magnet. Direction of field lines is from south to north inside the magnet.
- Field lines are concentric closed curves (elliptical)
- the relative strength of magnetic field is shown by degree of closeness of field lines. As field lines are crowded at the poles , magnetic strength is maximum near the poles.
- No two field lines cross each other. If two field lines cross then at the point of intersection, compass will show two direction of same location which is not possible.

Solenoid
Definition: A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of cylinder is called solenoid.
Characteristics: one end of the solenoid behaves as a magnetic north pole, while the other behaves as the south pole. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid. That is, the field is uniform inside the solenoid.
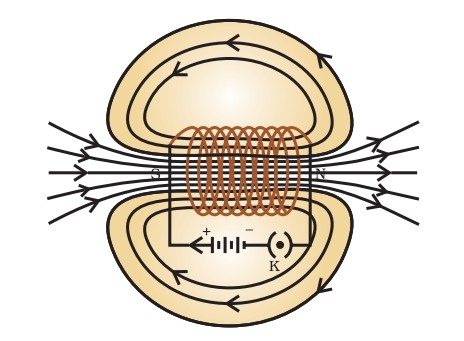
A strong magnetic field produced inside a solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material, like soft iron,
when placed inside the coil. The magnet so formed iscalled an electromagnet
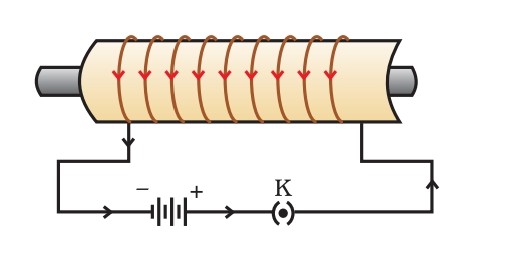
*Q*How to increase magnetic field in solenoid?
Ans. By following two ways magnetic field in solenoid can be increased:
- By increasing magnitude of current.
- by increasing number of turns.
Q. Can polarity in solenoid be reversed?
Ans. Yes. Polarity of solenoid can be reversed by changing direction of current.
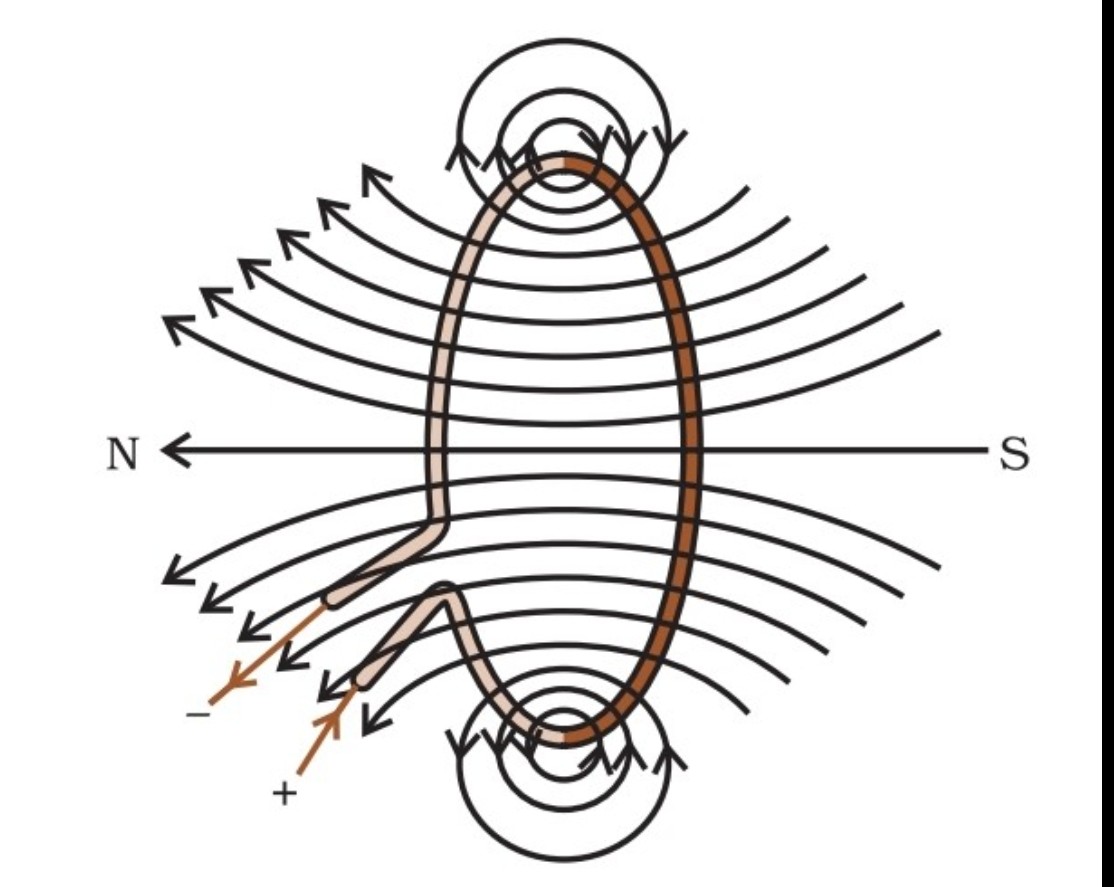
Magnetic field lines along current carrying Circular loop
Force on current carrying conductor in a magnetic field
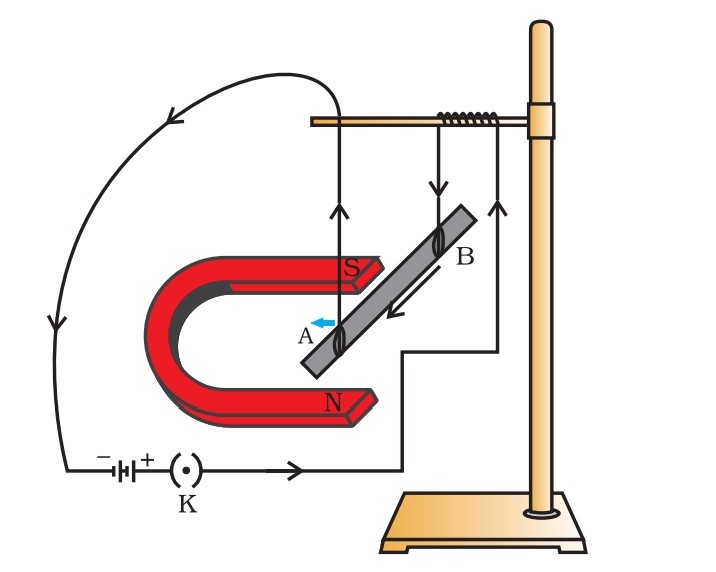
The displacement of the rod in the above activity suggests that a force is exerted on the current-carrying aluminium rod when it is placed in a magnetic field. It also suggests that the direction of force is also reversed when the direction of current through the conductor is reversed. Now change the direction of field to vertically downwards by interchanging the two poles of the magnet. It is once again observed that the direction of force acting on the current-carrying rod gets reversed. It shows that the direction of the force on the conductor depends upon the direction of current and the direction of the magnetic field. Experiments have shown that the displacement of the rod is largest (or the magnitude of the force is the highest) when the direction of current is at right angles to the direction of the magnetic field. Fleming’s left hand Rule can be used to find direction of force exerting on conductor.
Q. Compare AC and DC.
| AC | DC |
| 1. It stands for alternating current | it stands for direct current |
| 2. Produced by power stations and by ac generator. | produced by cell or battery and by dc generator. |
| can be transported to large distances | can not be transported to large distances |
| can not be stored | can be stored |
| Frequency of AC in India is 50Hz that means direction change 100 times in 1second. | do not change direction. |